- Do Not Try to Experiment
- The Socket: These can be seen in the form of AC MAINS power outlets over the electrical boards. The power fed into a socket is always via a switch as explained above. External appliances may be plugged into a socket and switched ON to operate, and vice versa. Sockets are available in 2 or 3 pin types. In 3-pin types the third or the top pin is provided for the earth or the ground connection. It helps in grounding or neutralizing any dangerous residual electrical potential that may be hanging over the connected appliance’s body.Main DPDT Switch: It may be considered as the entrance or the gateway for electricity and thus has to handle huge loads. It’s also a kind of switch but is much robust and designed to withstand high magnitudes of current through it. DPDT stands for Double Pole Double Throw as these may be operated manually to isolate both the wires of the supply line all at once for ultimate safety (Refer Diagram). It also incorporates an in-built Fuse to safeguard the whole house wiring in case of a short circuit.
 Electrical Load: Any electrical gadget that needs to be operated using electricity constitutes an electrical load. Every piece of electrical equipment from an incandescent bulb to the refrigerator that consumes electric power to remain operative is an electrical load.The next page will deal with the various home electrical wiring diagrams, so let's see how we proceed with them.
Electrical Load: Any electrical gadget that needs to be operated using electricity constitutes an electrical load. Every piece of electrical equipment from an incandescent bulb to the refrigerator that consumes electric power to remain operative is an electrical load.The next page will deal with the various home electrical wiring diagrams, so let's see how we proceed with them. Designing Home Wiring Layouts
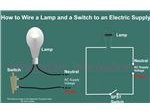
The following explanation will help you understand better how to design home wiring layouts:How to Wire a Switch and a Load (a Light Bulb) to an Electrical Supply: As can be seen in the diagram the wiring is pretty simple. The Phase is invariably applied to one terminal of the switch, the other terminal moves to one of the connections of the load, and the other point of the load continues to finish at the Neutral of the supply line. Toggling the switch will alternately switch the bulb ON and OFF.How to Connect Two Switches in Parallel to Operate a Single Load: In the above example if an additional switch is connected to the existing one in parallel, either of them may be used to switch ON the bulb. And if desired, one switch may be located far away for remote operation of the light. But here, to deactivate the load (Bulb), both the switches will need to switch OFF.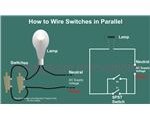 How to connect Two Switches in Series to Operate a Single Load: If two switches are connected in series to the above network (see the figure below)), both of them will need to be switched ON to energize the load, but, toggling OFF any one of the switches will be enough to extinguish the light.
How to connect Two Switches in Series to Operate a Single Load: If two switches are connected in series to the above network (see the figure below)), both of them will need to be switched ON to energize the load, but, toggling OFF any one of the switches will be enough to extinguish the light.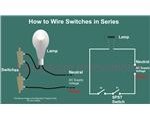 How to wire a Socket with a Switch to an Electrical Supply: The below given diagram shows a simple method of connecting a socket with a switch. Here, the Phase as usual and mandatorily is connected to one terminal of the switch and its other terminal is wired to the RIGHT hand side terminal of the socket. The LEFT hand side terminal of the socket goes to the Neutral line of the supply voltage.
How to wire a Socket with a Switch to an Electrical Supply: The below given diagram shows a simple method of connecting a socket with a switch. Here, the Phase as usual and mandatorily is connected to one terminal of the switch and its other terminal is wired to the RIGHT hand side terminal of the socket. The LEFT hand side terminal of the socket goes to the Neutral line of the supply voltage.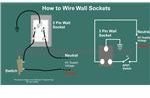 How to Interconnect a Switch, a Fan and a Fan Regulator to an Electrical Supply: With the help of the figure (shown below), one can easily see the simple concept of joining a fan, a fan regulator and a switch to an electrical supply. The idea is simple, just go on connecting each of them in series to one another. The diagram is self explanatory (Remember, the Phase always needs to be connected to the switch).
How to Interconnect a Switch, a Fan and a Fan Regulator to an Electrical Supply: With the help of the figure (shown below), one can easily see the simple concept of joining a fan, a fan regulator and a switch to an electrical supply. The idea is simple, just go on connecting each of them in series to one another. The diagram is self explanatory (Remember, the Phase always needs to be connected to the switch).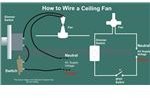 electrical$ worldThe basic home electrical wiring diagrams described above should have provided you with a good understanding. Hopefully this should help you in designing your own home wiring layouts independently. If in any sort of problem, feel free to exchange your thoughts with me (comments need moderation, and may take sometime to appear).
electrical$ worldThe basic home electrical wiring diagrams described above should have provided you with a good understanding. Hopefully this should help you in designing your own home wiring layouts independently. If in any sort of problem, feel free to exchange your thoughts with me (comments need moderation, and may take sometime to appear).
Thursday, September 24, 2015
what is difference between holding current and latching current?
what is difference between holding current and latching current?
LATCHING CURRENT is another name for gate trigger current -- it's a measure of
the minimum current you have to apply to the gate of an SCR to be guaranteed it
will turn on (given that there's a minimum voltage between anode and cathode).
Holding current is the specified minimum current that must be flowing from
anode to cathode (with no gate current) and still be guaranteed that the SCR
will not turn off.
As an example, the latching (gate trigger) current for a 2N5062 (logic level
SCR in TO-92 pkg) is 350 uA over the entire temp range, and the holding current
is10 mA over temp.
Saturday, August 29, 2015
Exact difference b/w between earthing, grounding and neutral?
Exact difference b/w between earthing, grounding and neutral?
Neutral
Neutral is return path for an AC circuit which is supposed to carry current in normal condition. This current may be because of many reasons, primarily because of phase current imbalance and some time because 3rd and 5th harmonics also.- Earthing
means connecting the dead part (it means the part which does not
carries current under normal condition) to the earth. For example
electrical equipment’s frames, enclosures, supports etc.
While grounding means connecting the live part (it means the part which carries current under normal condition) to the earth. For example neutral of power transformer.
- The purpose of earthing is to minimize risk of receiving an electric shock if touching metal parts when a fault is present.
While the purpose of grounding is the protections of power system equipment and to provide an effective return path from the machine to the power source. For example grounding of neutral point of a star connected transformer.
- Ground is a source for unwanted currents and also as a return path for main current some times. While earthing is done not for return path but only for protection of delicate equipments.
Design Your Own Home Wiring Layouts with These Basic Home Electrical Wiring Diagrams
Design Your Own Home Wiring Layouts with These Basic Home Electrical Wiring Diagrams.
Fundamentals of Household Wiring
Are
you planning to move into a new house and feel pretty excited about
doing some innovative electrical wiring there all by yourself? The idea
sounds great as that gives you the freedom to customize the design for
home wiring layout, and also help in saving quite a lot of money. But
this is not possible before you are well versed with the basics of
electrical wiring and know exactly how to chalk out correct home
electrical wiring diagrams.
In this article we will get acquainted with the various general
electrical components, their symbols and also study the different
fundamental electrical wiring configurations normally involved in every
domestic the wiring. But before that, let’s briefly look at what
electricity is.What is Electricity?
Electricity:
The power that we receive in our houses from power stations in the form
of alternating current and voltage is in fact the electricity. Any
electrical wiring is useless without electricity and thus it becomes the
life line of all electrical systems. Generally, these are either around
110 or 220 volts depending upon which part of the globe you are in.
Similarly its frequency will be approximately 60 and 50 Hertz
respectively. Its Main Line is termed as the Phase or Live while the
other receiving terminal is called the Neutral. It can be absolutely
FATAL to touch the Phase terminal whereas the Neutral is just the
opposite and won’t produce any effect.
Wednesday, July 1, 2015
Why Electrical Motor in KW insted of KVA & Transformer in KVA insted of KW
Why Electrical Motor in KW insted of KVA & Transformer in KVA insted of KW
There are two type of losses in a transformer;
1. Copper Losses
2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Copper losses ( I²R)depends on Current which passing through transformer winding while Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses depends on Voltage.
1. Copper Losses
2. Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses
Copper losses ( I²R)depends on Current which passing through transformer winding while Iron Losses or Core Losses or Insulation Losses depends on Voltage.
So the Cu Losses depend on the rating current of the load so the load type will determine the powerfactor P.F ,
Thats why the rating of Transformer in kVA,Not in kW.
Designer doesn’t know the actual consumer power factor while
manufacturing transformers and generators i.e. the P.F (Power factor) of
Transformer and Generator/Alternator depends on the nature of connected
load such as resistive load, capacitive load, and inductive load as
Motors, etc.
But
Motor has fixed Power factor, i.e. motor has defined
power factor and the rating has been mentioned in KW on Motor nameplate
data table. That’s why we are rated Motor in kW or HP (kilowatts/
Horsepower) instead of kVA.
In addition, Motor is a device which converts Electrical power into
Mechanical power. In this case, the load is not electrical, but
mechanical (Motor’s Output) and we take into the account only
active
power which has to be converted into mechanical load. Moreover, the
motor power factor does not depend on the load and it works on any P.F
because of its designSEE MORE REASON HERE
FIND US ON FACEBOOK
Sunday, February 8, 2015
Gate 2015 solutions
Gate 2015 solution
Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE
2015) exam was conducted on January 31, 1 and 7, 2015. The last phase
of exam will be conducted today; February 8,2015 during forenoon and
afternoon sessions.The first phase of the test covered disciplines like agriculture, mechanical, electronics and communications, and chemical engineering. Students found the difficulty level of the test to be average.
The GATE 2015 score will be valid for a period of three years from the date of announcement of results. All the papers in GATE 2015 will be held in online mode only and some examinations will be conducted in multiple sessions.
The online Computer Based Test (CBT) will be held for all the 22 papers. The online examination paper will contain some questions for which numerical answers must be keyed-in by the candidate using the virtual keypad. Rest of the questions shall be multiple choice questions (MCQ). Candidates will have to go through biometric (photograph and fingerprints) verification before the start of the examination.
What to know before entering the examination hall?
- Electronic diary, mobile phone, and any such electronic gadgets, blank papers, clip boards and log-tables will not be allowed in the examination venue
- You can use your own non-programmable calculator
- Bring the Admit Card at the test center along with at least one original (not photocopied/scanned copy) and valid (not expired) photo identification, whose details have been entered while filling the application
- Only one of the following photo-ids is permitted: Driving license, passport, PAN card, voter ID, Aadhaar UID, college ID, employee identification card, or a notarized affidavit with photo, signature, date of birth and residential address
- Photocopies of the identification document are not acceptable. Candidates will not be permitted to take the exam if the original and valid photo identification is not presented
- The test will also have numerical answers to some questions.
- Examination for some of the papers in GATE 2015 will be held in multiple sessions
click here for
Gate solution 2015
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)